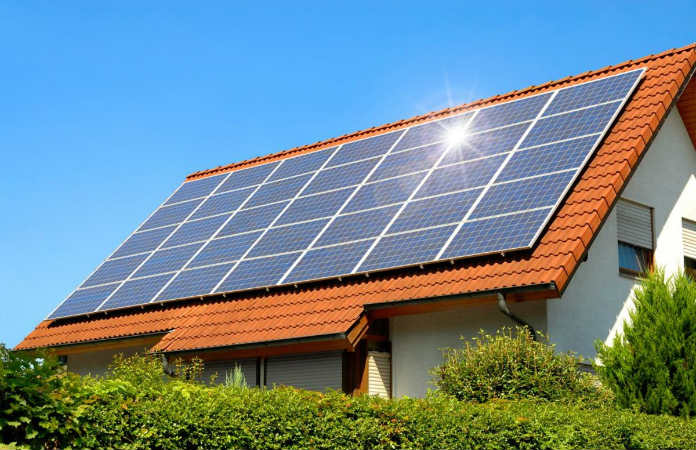
While traditional silicon-based solar panels remain the standard in many residential installations, new technology is expanding the options available to homeowners. Freedom Forever Solar, a residential solar provider specializing in customized, high-efficiency monocrystalline systems, focuses on delivering energy-efficient solutions tailored to individual homeowner’s needs. Thin-film solar panels, known for their flexibility and lightweight, are gaining traction for their ability to function in situations where conventional panels may be less effective.
These alternative panels aren’t designed to replace traditional modules in every case. Instead, they create new opportunities for homes with complex roof layouts, limited structural support, or specific aesthetic preferences. As demand grows for adaptable and sustainable energy solutions, thin-film solar is emerging as a valuable option for homeowners seeking personalized, performance-driven systems.
What Makes Thin-Film Solar Different?
Thin-film solar panels are constructed by placing one or more layers of photovoltaic material onto a substrate like glass, plastic, or metal. These layers are extremely thin, often just a few micrometers thick, and allow for greater flexibility in design and installation.
Unlike standard crystalline silicon panels, which are rigid and relatively heavy, thin-film panels can bend slightly and conform to a variety of surfaces. It gives them an edge in use cases where weight or space is limited.
Several types of thin-film technologies exist, including Cadmium Telluride (CdTe), amorphous silicon (a-Si) and Copper Indium Gallium Selenide (CIGS). Each type offers different performance characteristics, but all share the same core advantages of being lightweight and versatile.
Ideal Applications for Residential Settings
Thin-film panels shine in specific situations that may not be ideal for traditional rooftop installations. For example:
- Lightweight roofs: Some older or flat-roof homes cannot support the weight of conventional panels. Thin-film options offer a safer alternative that won’t compromise structural integrity.
- Aesthetic preferences: Because thin-film panels can be made with a uniform black appearance and laid flush with surfaces, homeowners who want a low-profile look often prefer them.
- Mobile or off-grid setups: RVs, tiny homes and other mobile living arrangements benefit from thin-film flexibility and lower weight.
- Unusual layouts: Homes with curved or angular roofs may benefit from thin-film’s ability to conform to non-standard shapes.
While these panels may not offer the same efficiency as monocrystalline silicon panels in high-output situations, they are often better suited for environments where space, weight or surface conditions are limiting factors.
Eco-Friendly Manufacturing and Materials
Another advantage of thin-film solar is its comparatively low environmental impact during production. Because less raw material is used and manufacturing temperatures are often lower, some thin-film panels have a smaller carbon footprint than traditional silicon panels.
In certain cases, these panels are also easier to recycle. With fewer bulky components and less silicon to reclaim, disposal or repurposing may be simpler at the end of the panel’s life cycle, though recycling processes still vary by manufacturer and region.
That said, homeowners should consider the full environmental profile of any solar product, including the source of materials, panel longevity and potential recycling availability in their area.
Comparing Performance and Longevity
While thin-film panels have improved significantly in recent years, they typically offer lower efficiency ratings than their silicon counterparts. This means more surface area is required to generate the same amount of electricity, an important consideration for homeowners with limited roof space.
Thin-film panels often perform better in low-light or high-temperature conditions, which can help balance out their lower peak efficiency. Their flexible nature also allows for installation in spots that might otherwise go unused.
Longevity varies by product type and manufacturer, but many thin-film panels now come with warranties similar to traditional panels, typically ranging from 10 to 25 years. It makes them a more viable option for long-term residential use than it was in previous generations.
Integration With Other Solar Technologies
While thin-film panels are typically used in commercial or specialized applications, hybrid systems that combine different solar technologies are gaining interest in unique residential needs. For example, high-efficiency panels may be installed on the sunniest sections of a roof, while alternative technologies can serve areas with shading or design limitations. These configurations are useful in maximizing available space and maintaining power consistency across varied conditions.
Freedom Forever reviews each home’s structure and energy goals to provide tailored system designs, primarily utilizing high-efficiency monocrystalline panels, to reflect local conditions and customer priorities. While their primary offerings focus on high-efficiency panel systems, their team helps homeowners explore optimized layouts and configurations to ensure long-term reliability and performance.
Considering Costs and Incentives
Thin-film solar panels are often less expensive to manufacture, which can translate to lower upfront costs in some cases. The lower efficiency means that installation costs, including labor and additional materials, may be higher per watt, depending on the application.
Homeowners interested in thin-film technology should discuss potential savings and performance expectations with their installer. Incentives like the federal Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC) generally apply regardless of panel type as long as the system meets eligibility standards.
It’s also worth checking local utility or state programs that might offer additional support for alternative solar technologies.
A Complementary Tool, not a Universal Solution
Thin-film solar is not positioned to replace standard panels in every situation, but it fills important gaps in residential solar adoption. By offering flexible installation, reduced weight and the potential for lower environmental impact, thin film provides more options for homeowners with specialized needs.
Its growing role in modular and hybrid solar systems reflects a broader trend toward flexibility and customization, allowing households to build energy systems that reflect their unique living environments.
Expanding the Possibilities of Solar Adoption
As solar energy becomes a larger part of household planning, thin-film technology expands the possibilities for who can benefit and how. From lightweight designs on aging rooftops to sleek, flush-mounted panels that preserve architectural aesthetics, thin film opens new doors for clean energy integration.
While these panels may not always be the most powerful per square foot, their adaptability and low-impact design make them an important tool in the next wave of residential solar.
With guidance from providers, homeowners can evaluate whether thin-film solar panels fit their energy goals, budget, and property features. As solar adoption grows, more diverse technology options mean more homes, no matter their size, shape or structure, can participate.